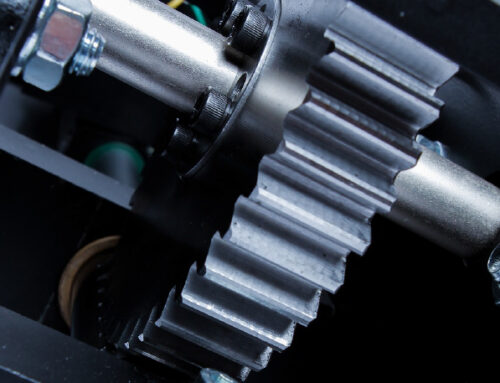
Gearbox alignment is crucial for optimal performance, extending the lifespan of machinery, preventing costly repairs, improving energy efficiency, and ensuring workplace safety. Unfortunately, alignment is often overlooked, leading to unnecessary downtime and maintenance issues.
Understanding gearbox misalignment—what it is, why it occurs, and how to prevent it—is essential for maintaining reliable equipment operation. Let’s dive into the details.
What Is Gearbox Alignment & Why Is It Important?
A properly functioning gearbox requires precise alignment with the motor and other moving parts, such as drive belts or crushers. The input and output shafts of the speed reducer must align perfectly with their corresponding drive units. When this alignment is off, the entire system becomes misaligned, which can lead to serious mechanical problems.

Why Is Misalignment an Issue?
Misalignment puts excessive stress on key components like shafts and couplings, causing premature wear and increasing the risk of failure. It also reduces efficiency and can create unsafe working conditions. Identifying and addressing different types of misalignment is vital for long-term reliability.
What Causes Gearbox Misalignment?
Angular Misalignment
Angular misalignment occurs when the input and output shafts are not aligned at the correct angle, creating a gap between them. This can be caused by improper installation, damaged housing, or manufacturing errors.
Causes of Angular Misalignment:
- Improper installation or assembly
- Damaged housing or mounting surfaces
- Parallel misalignment of shafts
- Manufacturing defects
Parallel Misalignment
This happens when two shafts are parallel but offset from each other. Common causes include incorrect shimming, worn bearings, or component defects.
Causes of Parallel Misalignment:
- Improper shimming during installation
- Worn or damaged bearings
- Manufacturing flaws in components
Combined Misalignment
When both angular and parallel misalignments occur simultaneously, it's called combined misalignment. This often results from installation errors, foundation settling, or component damage.
Causes of Combined Misalignment:
- Incorrect shimming
- Worn bearings
- Installation mistakes
- Foundation movement
- Component defects
Thermal Expansion Misalignment
Temperature changes can cause expansion or contraction of connected shafts, leading to misalignment if not accounted for during installation.
Causes of Thermal Misalignment:
- Environmental temperature fluctuations
- Inadequate thermal expansion considerations
- Material property variations
Soft Foot
Soft foot occurs when a gearbox doesn't sit evenly on its base due to uneven mounting or a short leg. This leads to uneven forces and misalignment.
Causes of Soft Foot:
- Uneven or deteriorated foundation
- Improper shimming
- Distorted housing
Resonance-Induced Misalignment
Resonance occurs when external vibrations match the natural frequency of the system, amplifying oscillations and potentially causing misalignment.
Causes of Resonance-Induced Misalignment:
- Insufficient damping
- Improper design
- Changes in operating conditions
Vibrations & Shock Loads
Prolonged vibration or sudden shock loads can gradually lead to misalignment. These forces can damage components and disrupt alignment over time.
Causes of Vibrations & Shock Loads:
- Vibrations from other machines
- Unbalanced rotating parts
- Worn-out bearings or gears
- Lack of maintenance
5 Tips for Preventing Common Misalignment Issues

1) Proper Installation & Mounting
Always follow manufacturer guidelines for installation and ensure all components are correctly aligned during setup.
2) Fix Damaged Parts
Replace worn or damaged components like bearings, seals, or gears to prevent misalignment. Explore our inventory of Falk parts or contact us directly for assistance.
3) Prioritize Routine Maintenance
Partner with a professional gearbox repair specialist to avoid common misalignment issues and extend the life of your equipment.
4) Properly Store Your Gearbox
Store gearboxes in a safe, stable environment to avoid internal damage or misalignment. Follow our storage tips for best results.
5) Perform Regular Alignment Checks
Use laser alignment systems to detect and measure misalignment accurately. These tools help ensure that your gearbox remains properly aligned over time.
Contact Our Falk Gearbox Motor Suppliers for Repair & Maintenance
Proper alignment and regular maintenance are key to enhancing the reliability and efficiency of your machinery while reducing costs and risks. Learn more about our Falk gearbox repair and renewal services or contact us for support. Our experts are available 24/7 to assist you with your specific needs.