Final drive,travel motor,excavator final drive,travel motor excavator,excavator travel motor,mini excavator JINING AOWEI MACHINE CO.,LIMITED , https://www.aoweimachine.com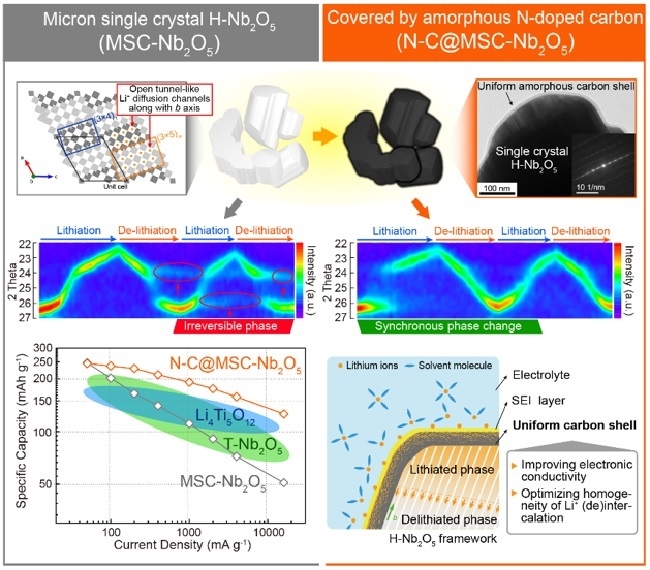
Dalian Chemical Institute's Strategy for Improving the Performance of High Specific Power Lithium Ion Battery Anode Materials
[ Instrument R & D of Instrumentation Network ] Recently, Li Xianfeng, Zhang Huamin, Zhang Hongzhang, researchers from the Energy Storage Technology Research Department of Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and the team of Associate Professor Tang Yongfu from Yanshan University have obtained the research on high specific power lithium ion battery anode materials new progress.
Niobium pentoxide has a higher specific capacity and a higher lithium ion phase diffusion coefficient, and can be used as a negative electrode material for high specific power lithium ion batteries to meet the technical development needs of rapid charging and rapid discharge. Among them, the high-temperature phase niobium pentoxide (that is, H-type Nb2O5) has the highest specific capacity, reaching 250 mAh / g (1.0 to 3.0 V vs Li + / Li), which has great potential for application development. However, during the charging and discharging process, the crystal structure of the material will continue to undergo irreversible changes, generating a type of crystal phase that is not suitable for the rapid insertion and extraction of lithium ions, thereby causing the capacity of lithium ion batteries to decay. This has become a major problem restricting the application of H-type Nb2O5 as a negative electrode material for lithium batteries.
The research team found that improving the transport uniformity of electrons and ions at the interface of the H-type Nb2O5 crystal surface is an effective strategy to solve the above problems. By coating the micron-level H-type Nb2O5 single crystal with a uniform amorphous carbon layer, the uniformity of the crystal structure change can be improved and the irreversibility of the crystal structure change can be suppressed. Carbon-coated H-type Nb2O5 can be cycled more than 1000 times under the condition of 2000 mA / g high current charge and discharge, which is nearly 10 times higher than the original, and its comprehensive performance is better than known Li4Ti5O12 materials and other Nb2O5 material. In addition, the team combined X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy and electrochemical characterization in situ to conduct an in-depth study on the insertion-extraction behavior of lithium ions in H-type Nb2O5 crystal materials to verify the interface of the amorphous carbon layer to the crystal surface Improvement of electron and ion transport uniformity and reversibility of structural changes.
Related research results were published in "Advanced Materials" (Advanced Materials). The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R & D Program, and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.